47 Degrees C To F
vittoremobilya
Sep 11, 2025 · 6 min read
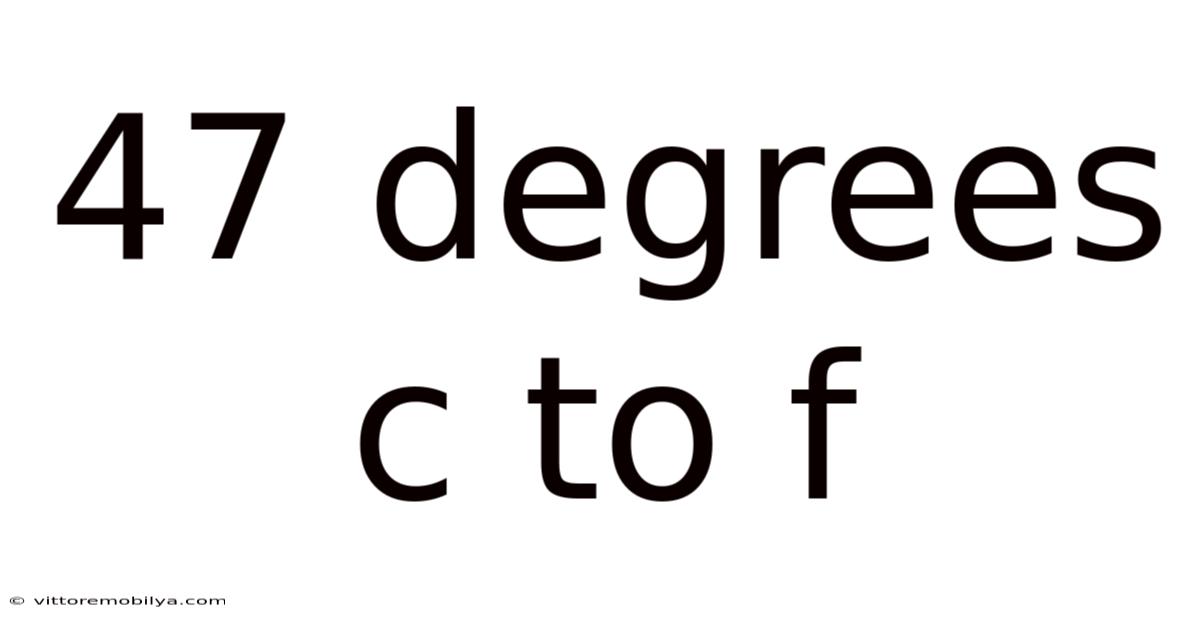
Table of Contents
Converting 47 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit: A Comprehensive Guide
Many of us encounter situations where we need to convert temperatures between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F). Whether you're checking a weather forecast from a foreign country, following a baking recipe, or simply understanding different temperature scales, knowing how to make this conversion is a valuable skill. This article will thoroughly explain how to convert 47 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, providing the formula, the calculation steps, and additional context to enhance your understanding of temperature conversion. We'll also delve into the history of these scales and explore practical applications of temperature conversions in everyday life.
Understanding Temperature Scales: Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two scales involved: Celsius and Fahrenheit.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is a metric unit of temperature. It's based on the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point of water at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. It's widely used in most of the world.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, this scale sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure. It's predominantly used in the United States.
The difference in the scales stems from the different reference points used to define them. Understanding this difference is crucial for accurate conversion.
The Formula for Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula states that to convert a Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit, you multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5 (or 1.8) and then add 32.
Step-by-Step Conversion of 47°C to °F
Now, let's apply the formula to convert 47 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit:
Step 1: Multiply by 9/5
47°C × 9/5 = 84.6°
Step 2: Add 32
84.6° + 32° = 116.6°F
Therefore, 47 degrees Celsius is equal to 116.6 degrees Fahrenheit.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
Understanding temperature conversions is essential in various aspects of daily life and professional fields:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion ensures the successful outcome of your culinary creations. Incorrect temperature can lead to undercooked or overcooked food.
-
Weather Forecasting: International weather reports may use Celsius, while local reports in the US might use Fahrenheit. Knowing how to convert allows you to understand the weather conditions accurately, regardless of the scale used.
-
Healthcare: Body temperature is often measured in both Celsius and Fahrenheit in different medical settings. Conversion between these scales is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. For example, a fever of 38°C (99.5°F) needs different treatment approaches than a fever of 40°C (104°F).
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes rely on precise temperature control. Accurate conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is vital for maintaining optimal operational efficiency and product quality. Think about industries like metallurgy, chemical processing, and pharmaceuticals.
-
Scientific Research: Scientific experiments often involve precise temperature control and measurement. The ability to seamlessly convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is crucial for ensuring consistency and reproducibility of results.
-
Travel and Tourism: Knowing how to convert temperatures will help you pack appropriate clothing for your travel destination. A temperature of 25°C (77°F) might feel warm in one place but cool in another depending on other weather conditions and personal sensitivity.
The History of Temperature Scales
The development of Celsius and Fahrenheit scales reflects the evolution of scientific understanding of temperature.
-
Fahrenheit Scale: Created by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, the Fahrenheit scale was initially based on three reference points: the freezing point of a brine solution (0°F), the freezing point of water (32°F), and the human body temperature (96°F). While the initial reference points were somewhat arbitrary, the scale gained widespread use, especially in the United States.
-
Celsius Scale: Also known as the centigrade scale, the Celsius scale was developed by Anders Celsius in 1742. It's a more straightforward system, using 0°C for the freezing point of water and 100°C for its boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure. This makes it more intuitive and scientifically consistent.
Over time, the Celsius scale has gained preference globally due to its simplicity and alignment with the metric system. However, the Fahrenheit scale continues to be used in some parts of the world, particularly in the United States.
Why are there two different scales?
The existence of both Celsius and Fahrenheit scales highlights the historical development of scientific measurement. Different scientists and countries adopted different scales, and these scales became entrenched over time. While efforts have been made to standardize on a single system (Celsius, largely), the persistence of both reflects the inertia of established practice.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Temperature
The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a simple calculation, but a deeper understanding of temperature itself is crucial. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Higher kinetic energy means higher temperature, resulting in faster particle movement. This relates to several concepts:
-
Heat Transfer: Heat always flows from a warmer object to a cooler object. This is crucial in understanding phenomena like cooking, refrigeration, and even weather patterns.
-
Thermal Equilibrium: When two objects of different temperatures come into contact, heat will flow until both reach the same temperature, known as thermal equilibrium.
-
Specific Heat Capacity: Different materials require different amounts of heat energy to raise their temperature by a certain degree. This property, called specific heat capacity, influences how quickly a material heats up or cools down.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the conversion formula (°C × 9/5) + 32?
A: This formula is derived from the relationship between the freezing and boiling points of water in both scales. The ratio 9/5 accounts for the difference in the scale's size (100 degrees Celsius versus 180 degrees Fahrenheit between freezing and boiling points of water). Adding 32 adjusts for the different zero points of the two scales.
Q: Can I convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A: Yes, the reverse conversion formula is: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Q: Are there other temperature scales?
A: Yes, besides Celsius and Fahrenheit, there's the Kelvin scale, which is an absolute temperature scale. Zero Kelvin represents absolute zero, the theoretical lowest possible temperature.
Q: What are some common mistakes when converting temperatures?
A: A common mistake is to forget to add 32 after multiplying by 9/5 (when converting from Celsius to Fahrenheit) or to perform the operations in the wrong order. Always follow the order of operations (multiplication before addition).
Conclusion
Converting 47 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit (116.6°F) is a straightforward process using the formula °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32. This conversion, however, represents a broader understanding of temperature scales, their historical development, and practical applications in everyday life. From cooking to weather forecasting to scientific research, the ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a valuable skill with wide-ranging uses. Understanding the underlying principles behind these scales and the concept of temperature itself further enhances this knowledge. Remember to practice these conversions to improve your understanding and proficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Instagram Chat Bubble Yellow Corner
Sep 11, 2025
-
Bf Kisses Me In Bed
Sep 11, 2025
-
How Much Rainfall Is 9 3mm
Sep 11, 2025
-
Nude In Front Of Family
Sep 11, 2025
-
Jobs That Require Wearing Diapers
Sep 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 47 Degrees C To F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.